mpls TE con definizione e configurazioni per signaling e constraints in cisco tecnology e tante simulazioni di fault-link and fault-node con output di verifica
19.04 2020 | by massimilianoQuesto documento si prefigge di cavalcare i vari step di configurazione e definizione per gli aspetti di signaling e constraints […]
https://www.ingegnerianetworking.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/mpls-ex1-044.PNG
Questo documento si prefigge di cavalcare i vari step di configurazione e definizione per gli aspetti di signaling e constraints presenti in una rete di tipo MPLS Traffic Engineering
Architettura fisica di riferimento è la seguente:
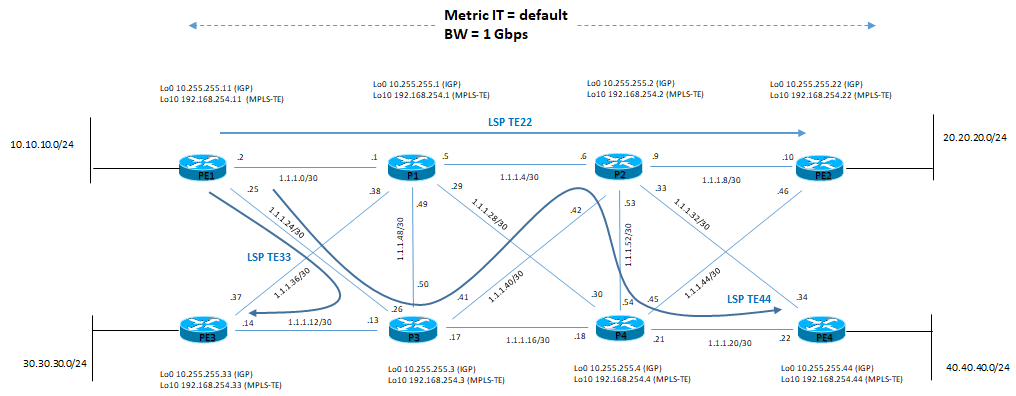
Architettura logica di riferimento è la seguente:
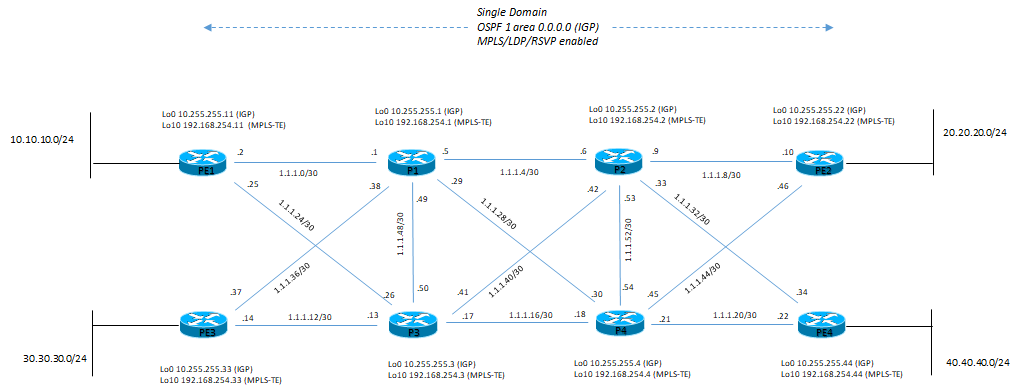
Dopo una configurazione base MPLS si riportano alcuni output (in grassetto le cose di rilievo):
|
PE1#show mpls ldp neighbor
|
PE1#show mpls forwarding-table |
|
PE1#show mpls ldp neighbor Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.1:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.11:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.1.646 – 192.168.254.11.32833 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 150/151; Downstream Up time: 01:41:06 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/0.2, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.1 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.29 10.255.255.1 192.168.254.1 1.1.1.49 Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.3:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.11:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.3.646 – 192.168.254.11.22796 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 103/109; Downstream Up time: 00:58:24 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/0.24, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.26 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.50 10.255.255.3 192.168.254.3 1.1.1.13 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.17 1.1.1.41 |
PE1#show mpls forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface 16 Pop Label 192.168.254.1/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 17 Pop Label 10.255.255.1/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 18 Pop Label 1.1.1.36/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 19 Pop Label 1.1.1.48/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 Pop Label 1.1.1.48/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 20 Pop Label 1.1.1.28/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 21 Pop Label 1.1.1.4/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 22 19 192.168.254.33/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 27 192.168.254.33/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 23 20 10.255.255.33/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 24 10.255.255.33/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 24 Pop Label 1.1.1.12/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 25 Pop Label 192.168.254.3/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 26 Pop Label 10.255.255.3/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 27 24 192.168.254.4/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 28 192.168.254.4/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 28 25 192.168.254.2/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 29 192.168.254.2/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26
29 26 10.255.255.4/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 30 10.255.255.4/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 30 27 10.255.255.2/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 31 10.255.255.2/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 31 Pop Label 1.1.1.40/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 32 29 1.1.1.52/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 33 1.1.1.52/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 33 Pop Label 1.1.1.16/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 34 31 192.168.254.22/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 34 192.168.254.22/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 35 32 10.255.255.22/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 35 10.255.255.22/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 36 33 1.1.1.8/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 36 1.1.1.8/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 37 35 1.1.1.20/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 37 1.1.1.20/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 38 34 1.1.1.44/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 38 1.1.1.44/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 39 36 192.168.254.44/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 39 192.168.254.44/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 40 37 10.255.255.44/32 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 40 10.255.255.44/32 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 41 38 1.1.1.32/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.1 41 1.1.1.32/30 0 Gi0/0.24 1.1.1.26 PE1#
|
|
P1#show mpls ldp neighbor
|
P1#show mpls forwarding-table |
|
P1#show mpls ldp neighbor Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.11:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.1:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.11.32833 – 192.168.254.1.646 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 86/84; Downstream Up time: 00:43:54 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/0.2, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.2 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.25 10.255.255.11 192.168.254.11 10.10.10.1 Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.33:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.1:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.33.27240 – 192.168.254.1.646 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 64/65; Downstream Up time: 00:27:23 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/0.36, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.37 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.14 1.1.1.37 10.255.255.33 192.168.254.33 30.30.30.1 Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.3:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.1:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.3.57241 – 192.168.254.1.646 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 63/72; Downstream Up time: 00:24:41 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/2, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.50 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.50 10.255.255.3 192.168.254.3 1.1.1.13 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.17 1.1.1.41 Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.2:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.1:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.2.17977 – 192.168.254.1.646 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 34/34; Downstream Up time: 00:01:25 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/1.4, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.6 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.53 10.255.255.2 192.168.254.2 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.42 Peer LDP Ident: 192.168.254.4:0; Local LDP Ident 192.168.254.1:0 TCP connection: 192.168.254.4.11016 – 192.168.254.1.646 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 35/39; Downstream Up time: 00:00:35 LDP discovery sources: GigabitEthernet0/1.28, Src IP addr: 1.1.1.30 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.54 10.255.255.4 192.168.254.4 1.1.1.18 1.1.1.30 1.1.1.21 1.1.1.45 P1#
|
P1#show mpls forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface 16 Pop Label 1.1.1.24/30 0 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.2 Pop Label 1.1.1.24/30 0 Gi0/2 1.1.1.50 17 Pop Label 10.255.255.11/32 32267 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.2 18 Pop Label 192.168.254.11/32 1344 Gi0/0.2 1.1.1.2 19 Pop Label 192.168.254.33/32 1096 Gi0/0.36 1.1.1.37 20 Pop Label 10.255.255.33/32 23428 Gi0/0.36 1.1.1.37 21 Pop Label 1.1.1.12/30 0 Gi0/0.36 1.1.1.37 Pop Label 1.1.1.12/30 0 Gi0/2 1.1.1.50 22 Pop Label 192.168.254.3/32 3872 Gi0/2 1.1.1.50 23 Pop Label 10.255.255.3/32 0 Gi0/2 1.1.1.50 24 Pop Label 192.168.254.4/32 534 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 25 Pop Label 192.168.254.2/32 1334 Gi0/1.4 1.1.1.6 26 Pop Label 10.255.255.4/32 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 27 Pop Label 10.255.255.2/32 0 Gi0/1.4 1.1.1.6 28 Pop Label 1.1.1.40/30 0 Gi0/1.4 1.1.1.6 Pop Label 1.1.1.40/30 0 Gi0/2 1.1.1.50 29 Pop Label 1.1.1.52/30 0 Gi0/1.4 1.1.1.6 Pop Label 1.1.1.52/30 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 30 Pop Label 1.1.1.16/30 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 Pop Label 1.1.1.16/30 0 Gi0/2 1.1.1.50 31 36 192.168.254.22/32 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 32 38 10.255.255.22/32 10232 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 33 40 1.1.1.8/30 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 34 Pop Label 1.1.1.44/30 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 35 Pop Label 1.1.1.20/30 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 36 35 192.168.254.44/32 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 37 37 10.255.255.44/32 10764 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 s38 39 1.1.1.32/30 0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30 P1# |
Tutti gli altri nodi sia essi PE router che P router hanno un medesimo output visto per PE1 e P1 nelle tabelle di cui sopra
TRAFFIC-ENGINEERING OPERATION:
MPLS-TE coinvolge i seguenti items:
– link information distribution
– path computation
– LSP signaling
– traffic selection
Link Information Distribution:
MPLS-TE utilizza una estensione per IGP [ sia esso OSPF (LSA type 10 opaque) che ISIS (TLV) ] Link-State per la distribuzione di topologia della rete; un qualsiasi nodo LSR (label switch router) necessità di queste informazioni per performare le opportune constraint di routing.
Questi constraints (in italiano vincoli) sono riferite alla conoscenza dei parametri di link correnti necessari per la costruzione di un corretto LSP TED (traffic-engineering database); questo database è separato dal normale topology di rete che un nodo LSP costruisce su base hop-by-hop destination based-routing
Si ricorda che i protocolli di routing IGP quali OSPF e ISIS, senza le dovute estensioni non sono adeguati alle esigenze di una politica IT in quanto:
i protocolli IGP :
utilizzano algoritmi Shortest Path First (SPF)
utilizzano metriche additive
sono topology-oriented
i protocolli IGP non considerano:
la disponibilità di banda sui vari link (stato di congestione dei link)
le caratteristiche del traffico
MPLS-TE, quindi, introduce degli attributi ricondicibili alla disponibilità di banda (available bandwidth), un gruppo amministrativo (flag) e di una metrica TE.
– ogni link ha otto quantità di banda disponibile corrispondenti agli otto livelli di priorità che un LSP-TE può avere, anche conosciute come Class-Type (CT)
– un gruppo amministrativo (flag) è un meccanismo di classificazione che definisce regole di link di inclusione oppure esclusione
– la metrica TE è simile alla metrica IGP ma è utilizzata come un secondo link-metric per funzionalità di ottimizzazione del link (path optimization)
La tabella di cui sotta evidenzia i link attributi distribuiti per TE:

MPLS-TE sta nel fatto che per avere un routing efficiente bisogna instradare il traffico lungo percorsi a costo minimo rispettando contemporaneamente determinati vincoli (constraints) sullo sfruttamento delle risorse di rete.
Uno volta determinato il percorso ottimo serve poi un protocollo di segnalazione tramite il quale informare tutti gli LSR interessati della necessità di allocare un tunnel TE con determinati requisiti di banda e/o amministrativi e quindi di associare delle etichette MPLS per definire il/gli LSP corrispondenti.
In ambito IETF sono stati standardizzati due protocolli di segnalazione:
RSVP-TE (ReSerVation Protocol with Tunneling Extension).
CR-LDP (Constraint-based LSP setup using LDP)
Path Computation:
Un nodo LSR performa un path computation per TE-LSP utilizzando il TED (topology database);
CSPF (Constraint-based Shortest Path First) è un’estensione dell’algoritimo SPF che lavora andando ad eliminare tutta una serie di parametri che non soddisfano i vincoli dettati dal tunnel LSP-TE.
CSFP per il best-path può utilizzare la metrica IGP come pure quella TE, il valore di bandwidth ed un peso amministrativo ma non garantisce completamente le risorse ottimali messe a disposizione per il traffico ma viene considerato come approssimazione.
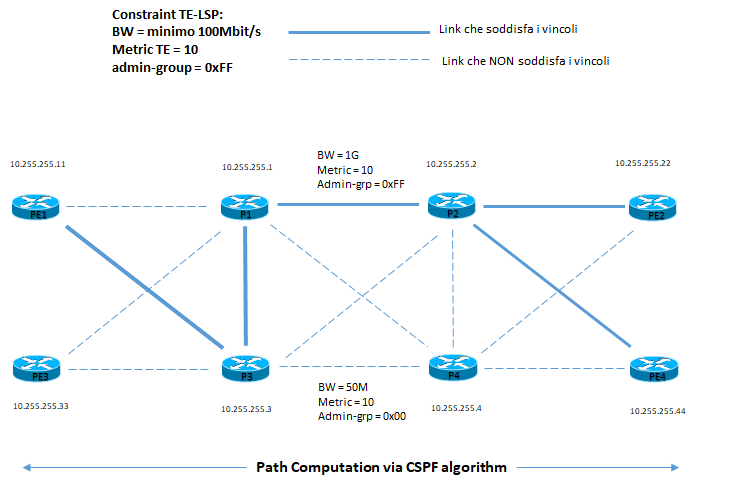
Il path computation in un contesto di multi-area oppure inter-AS coinvolge solo una parziale visione della topologia di rete per la costruzione end-to-end di un TE-LSP.
Quando un nodo headend (ingresso) ha una visione parziale della topologia di rete, può specificare un percorso come una lista di predefiniti router di bordo come ABR nel caso di inter-area oppure di ASBR in caso di multi-AS.
Il processo di segnalazione, quindi, si performa solo a livello di boundary router LSR che possono avere una visione completa tra differenti aree oppure tra differenti autonomous system, affinchè ci possa essere un tunnel LSP di tipo end-to-end (tra sorgente e destinazione).
Segnalazione di un LSP-TE (RSVP):
MPLS-TE richiede il protocollo RSVP-TE (Reservation Protocol) per la segnalazione di un tunnel LSP-TE
RSVP ha cinque stati che sono:
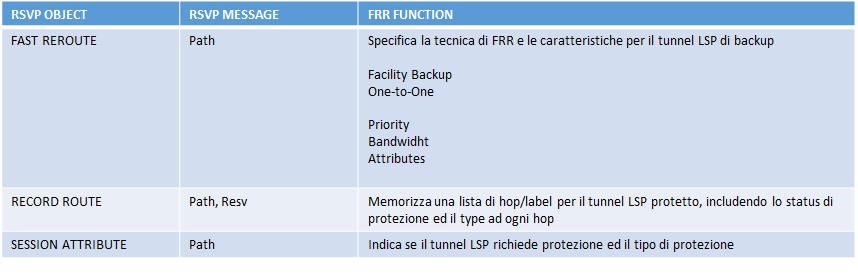
- Label Request: utilizzato nei messaggi di tipo “path” per la richiesta di una label binding ad ogni hop
- Label: utilizzata nei messaggi di tipo “resv” per performare una distribuzione di labelling utilizzando la modalità “downstream on demand” tra i nodo di rete LSR
- Label Explicit: contiene una lista di hop che definiscono i percorsi segnalati che il traffico dovrà attraversare
- Record Route: è una collezione di informazioni riguardo gli hop e le label distribuite segnalate lungo un determinato percorso
- Session Attribute: è una lista di attributi richiesti per un determinato LSP quali ad esempio priority, protection, etc…)
Traffic Selection:
Il traffico può partire solo da un nodo headend, quindi la decisione di un path per un determinato traffico è compito del nodo di ingresso della rete MPLS e la selezione può essere fatta in modo statico o dinamico.
Fast-Reroute:
MPLS-TE supporta un meccanismo di recovery di un LSP-TE su base FRR (Fast Re-Route)
FRR lavora sulla base di un pre-segnalato path di backup LSP-TE, rispetto al primario ed in caso di fault di quest’ultimo un nodo è in grado di commutare (reroute appunto) il traffico sul path di backup.
Non vi sono delay nella propagazione del fault e nessun delay nella ricomputazione/segnalazione del path; FRR può re-ruotare il traffico in tens of milliseconds (RFC4090).
MPLS TE FRR offre due tecniche di protezione:
- – facility backup: utilizza lo stack di label (label stacking) per re-ruotare multipli LSP protetti con un singolo tunnel LSP di backup
- – one-to-one backup: questo approccio, invece, non usa il label stacking ed ogni LSP-TE in protezione richiede un dedicato tunnel LSP-TE di backup
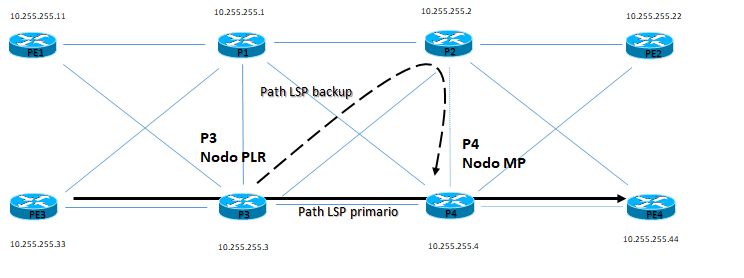
MPLS FRR introduce il ruolo di PLR (Point of Local Repair) e di MP (Merge Point):
– PLR ha sempre un tunnel di backup pre-segnalato ed è sempre il nodo headend del path di backup
- – MP è il nodo dove termina il tunnel di backup e ricongiunge il nodo di destinazione durante la fase di fault in corso come da tunnel originale
MPLS FRR utilizza i seguenti object RSVP:
MPLS-TE FRR può usare un metodo globale oppure locale di restoration di un tunnel LSP protetto come risultato di un network failure
L’approccio globale fa leva a livello headend node per il rerouting di un LSP protetto; questo significa che quando un fault si verifica il PLR trasmette un Path-Error message verso il nodo headend del tunnel protetto.
Il nodo headend inoltre può venire a conoscenza del fault, oltre che per la segnalazione di cui sopra via RSVP, anche via IGP update se il fault avviene nella stessa area/dominio IGP
Appena il nodo headend è ha conoscenza del fault può re-ruotare il traffico verso il tunnel di backup.
Con il metodo locale è il nodo PLR che re-ruota il traffico verso il tunnel LSP di backup durante la fase di fault; quando il facility fault ritorna nelle condizioni normali, il PLR torna a segnalare il tunnel primario protetto attraverso il percorso originale
Link Protection:
Link Protection utilizza un LSP-TE di backup destinato al PLR next-hop (NHOP); quando un nodo segnala un LSP-TE con link-protection, tutti i nodi lungo il percorso cercano di associare il tunnel LSP-TE con un backup tunnel verso il NHOP downstream (il tunnel di backup potrebbe già esistere oppure un nodo può provare a ricalcolarlo con un percorso possibile e segnalarlo).
Qualsiasi nodo che “trova” un LSP-TE di backup diventa un potenziale PLR e segnala la sua disponibilità in termini di protezione utilizzando il Record-Route.
Quando un link fallisce, il nodo PLR re-ruota tutti gli LSP-TE che identifica verso il tunnel di backup e questo processo stabilisce un pushing della label del tunnel di backup on-top allo stack di labels precedentemente creato con il tunnel primario (cioè prima del fault).
Link Protection lavora anche come protezione contro il failure di un SLRG (shared-risk link groups); questo significa che ci sono casi in cui multipli links in una rete possono avere un’alta probabilità di errore/fault allo stesso tempo.
Generalmente questi links condividono la stessa architettura di tipo layer 2, layer 1)
In questo caso il nodo PLR impara le condizioni di questi SLRG dinamicamente dal protocollo IGP con le sue estensioni oppure attraverso configurazioni locali.
Node Protection:
Node Protection utilizza un LSP-TE di backup destinato al PLR next-next hop (NNHOP); quando un nodo segnala un LSP-TE con node protection, i nodi lungo il percorso provano ad associare questo tunnel con un LSP-TE di backup verso il NNHOP downstream.
Le funzionalità viste sopra valgono anche per il Node Protection.
per maggiori dettagli su una simulazione di analisi link e node protection vedi: https://www.massimilianosbaraglia.it/routing/mpls/mpls-traffic-engineering/analisi-flusso-di-traffico-in-un-backbone-mpls-ip-considerando-metric-it-cspf-rsvp-link-protection-node-protection
Cosa sono gli attribute-flags per un traffico TE:
Sono indicati con un valore nel range 0x0 0xFFFFFFFF (vettore booleano) e rappresentano vincoli di inclusione ed esclusione per un determinato percorso.
In pratica si riferiscono a classi amministrative anche conosciute come colori e sono definite in modo arbitrario da un amministratore di rete attraverso un vettore booleano su parametri quali proprietà [ dove il bit = 1 significa che appartiene ad una determinata classe ed il bit = 0 significa che non appartiene (i bit vanno da zero quello più significativo a 31 quello meno significativo) ] ed affinità [ dove il bit = 1 significa proprietà di interesse ]
– quando il vettore Proprietà è uguale al vettore Affinità allora un collegamento è incluso
– quando il vettore Proprietà è differente dal vettore Affinità allora il collegamento è escluso.
per maggiori dettagli di come funziona questa definizione di classi amministrative o colori vedi: https://www.massimilianosbaraglia.it/routing/mpls/mpls-teoria/mpls-classi-di-amministrazione-colori-proprieta-and-affinita
Come si attribuisce una Priorità su base Setup ed Holding:
La priorità definisce l’ordine con il quale avviene la selezione del cammino al momento dell’instaurazione dei un LSP-TE (tunnel)
L’attributo di preemption (prelazione) determina se un tunnel-TE può sottrarre banda ad un altro tunnel-TE già attivo su un particolare cammino; la preemption può essere usata per assicurare che LSP-TE ad alta priorità vengano sempre instradati sui cammini più favorevoli
La preemption può essere usata per realizzare varie politiche di riconfigurazione dei cammini in caso di guasto
– L’attributo Setup è utile quando vogliamo dare un ordine di priorità a differenti flussi di traffico in ingresso ad un tunnel TE con specifiche risorse assegnate
– L’attributo Holding indica la possibilità per un flusso di traffico stabilito con determinate risorse di essere eliminato o reinstradato per dare posto ad un flusso con priorità superiore
– I valori di entrambi questi due attributi sono compresi tra 0 e 7, dove il più basso (zero) rappresenta una priorità maggiore rispetto al più alto (sette)
All’atto dell’instaurazione, la banda richiesta da un TT può essere allocata su un link se:
la banda è disponibile (libera)
mediante l’abbattimento di un tunnel-TE già instaurati che hanno un valore della holding priority inferiore alla setup priority del Tunnel da instaurare
Esempio di applicazione setup – holding:
– un flusso di traffico con Setup = 7 e Holding = 0 ha una priorità di ingresso più basso (una volta instradato non può essere più eliminato)
– due flussi di traffico con Setup = 1 e Holding = 7 durante la fase di segnalazione possono cadere in un loop che porta inevitabilmente all’impossibilità di stabilire flussi di traffico
NOTE di Configurazione:
– Mai configurare un valore di setup migliore (quindi con un valore più basso) rispetto al valore di holding causa la possibilità di innescare un loop di segnalazione
– E’ possibile avere, invece, valori di setup maggiore rispetto a quello di holding con una priorità di setup inferiore alla priorità di holding (ad esempio setup = 7 ed holding = 0) ed in questo caso un flusso di traffico ha priorità di ingresso più bassa ma una volta instradata è impossibile eliminarlo.
ENABLE MPLS-TE on Node (configurazione minima di base):
|
PE1
|
PE2 |
|
ip vrf PIPPO rd 65100:10 route-target export 65100:10 route-target import 65100:10 ! interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.11 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 ip rsvp bandwidth ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.24 mpls traffic-eng backup-path Tunnel22 ip rsvp bandwidth interface GigabitEthernet0/3 description LAN10 ip vrf forwarding PIPPO ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback0 passive-interface Loopback10 router bgp 65100 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor 192.168.254.22 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.22 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.33 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.33 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.44 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.44 update-source Loopback10 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 192.168.254.22 activate neighbor 192.168.254.22 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.33 activate neighbor 192.168.254.33 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.44 activate neighbor 192.168.254.44 send-community extended exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf PIPPO redistribute connected exit-address-family |
ip vrf PIPPO rd 65100:10 route-target export 65100:10 route-target import 65100:10 ! interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.22 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/2.8 interface GigabitEthernet0/3 description LAN20 ip vrf forwarding PIPPO ip address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 router bgp 65100 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor 192.168.254.11 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.11 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.33 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.33 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.44 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.44 update-source Loopback10 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 192.168.254.11 activate neighbor 192.168.254.11 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.33 activate neighbor 192.168.254.33 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.44 activate neighbor 192.168.254.44 send-community extended exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf PIPPO redistribute connected exit-address-family ! |
|
P1
|
P2 |
|
interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.1 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 interface GigabitEthernet0/1.4 router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 |
interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.2 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/1.4 interface GigabitEthernet0/3 router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 |
|
PE3
|
PE4 |
|
ip vrf PIPPO rd 65100:10 route-target export 65100:10 route-target import 65100:10 ! interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.33 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/0.12 interface GigabitEthernet0/3 description LAN30 ip vrf forwarding PIPPO ip address 30.30.30.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 router bgp 65100 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor 192.168.254.11 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.11 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.22 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.22 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.44 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.44 update-source Loopback10 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 192.168.254.11 activate neighbor 192.168.254.11 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.22 activate neighbor 192.168.254.22 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.44 activate neighbor 192.168.254.44 send-community extended exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf PIPPO redistribute connected exit-address-family ! |
ip vrf PIPPO rd 65100:10 route-target export 65100:10 route-target import 65100:10 ! interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.44 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/2.20 interface GigabitEthernet0/3 description LAN40 ip vrf forwarding PIPPO ip address 40.40.40.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 ! router bgp 65100 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor 192.168.254.11 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.11 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.22 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.22 update-source Loopback10 neighbor 192.168.254.33 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.254.33 update-source Loopback10 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 192.168.254.11 activate neighbor 192.168.254.11 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.22 activate neighbor 192.168.254.22 send-community extended neighbor 192.168.254.33 activate neighbor 192.168.254.33 send-community extended exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf PIPPO redistribute connected exit-address-family ! |
|
P3
|
P4 |
|
interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.3 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/0.12 interface GigabitEthernet0/1.16 router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 |
interface loopback10 description MPLS-TE-Loop ip address 192.168.254.4 255.255.255.255 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! mpls traffic-eng tunnels ! ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction interface GigabitEthernet0/1.16 interface GigabitEthernet0/3 ! router ospf 1 passive-interface Loopback10 |
La suddetta configurazione prevede i minimi step di attivazione MPLS-TE ma vediamo di seguito alcuni comandi utile per:
LINK-ATTRIBUTE:
La configurazione dei link-attribute prevede i seguenti comandi:
mpls traffic-eng administrative-weight
mpls traffic-eng attribute-flags
ip rsvp bandwidth
Come prerequisito è necessario abilitare sotto interfaccia il comando mpls traffic-eng tunnels, e senza una configurazione esplicita dei comandi di cui sopra abbiamo dei parametri di default che sono:
administrative weight è il valore di metrica IGP (di default)
attribute-flags = 0
rsvp bandwidth = 75 percent del valore di capacità della interfaccia fisica e senza il comando “ip rsvp bandiwidth” il valore di BW e pari a zero
Per verificare le informazioni che riguardano il link distribution si può utilizzare il seguente comando con relativo output:
|
PE1 |
P1 |
| PE1#show mpls traffic-eng link-management advertisements Flooding Status: ready Configured Areas: 1 IGP Area[1] ID:: ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 System Information:: Flooding Protocol: OSPF Header Information:: IGP System ID: 10.255.255.11 MPLS TE Router ID: 192.168.254.11 Flooded Links: 2 Link ID:: 0 (GigabitEthernet0/0.2) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.2 Designated Router: 1.1.1.2 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 Link ID:: 1 (GigabitEthernet0/0.24) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.25 Designated Router: 1.1.1.25 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 PE1# |
P1#show mpls traffic-eng link-management advertisements Flooding Status: ready Configured Areas: 1 IGP Area[1] ID:: ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 System Information:: Flooding Protocol: OSPF Header Information:: IGP System ID: 10.255.255.1 MPLS TE Router ID: 192.168.254.1 Flooded Links: 5 Link ID:: 0 (GigabitEthernet0/0.2) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.1 Designated Router: 1.1.1.2 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 Link ID:: 1 (GigabitEthernet0/0.36) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.38 Designated Router: 1.1.1.38 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 Link ID:: 2 (GigabitEthernet0/1.4) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.5 Designated Router: 1.1.1.5 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 Link ID:: 3 (GigabitEthernet0/1.28) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.29 Designated Router: 1.1.1.29 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 Link ID:: 4 (GigabitEthernet0/2) Link Subnet Type: Broadcast Link IP Address: 1.1.1.49 Designated Router: 1.1.1.49 TE metric: 1 IGP metric: 1 SRLGs: None Physical Bandwidth: 1000000 kbits/sec Res. Global BW: 750000 kbits/sec Res. Sub BW: 0 kbits/sec Downstream:: Global Pool Sub Pool ———– ———- Reservable Bandwidth[0]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[1]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[2]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[3]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[4]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[5]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[6]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Reservable Bandwidth[7]: 750000 0 kbits/sec Attribute Flags: 0x00000000 P1# |
|
PE1
|
P1 |
|
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng topology My_System_id: 10.255.255.11 (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) Signalling error holddown: 10 sec Global Link Generation 42
IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.1 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0)
link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.2, nbr_node_id:3, gen:8 frag_id 8, Intf Address:1.1.1.1 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.3, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.3 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.25, nbr_node_id:11, gen:29 frag_id 10, Intf Address:1.1.1.26 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.4, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.4 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.17, nbr_node_id:16, gen:38 frag_id 8, Intf Address:1.1.1.18 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.11, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.11 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.2, nbr_node_id:3, gen:2 frag_id 11, Intf Address:1.1.1.2 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.22, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.22 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.9, nbr_node_id:7, gen:17 frag_id 11, Intf Address:1.1.1.10 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.33, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.33 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.38, nbr_node_id:9, gen:20 frag_id 13, Intf Address:1.1.1.37 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.44, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.44 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.33, nbr_node_id:21, gen:41 frag_id 13, Intf Address:1.1.1.34 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 1.1.1.2, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.11, nbr_node_id:1, gen:4 IGP Id: 1.1.1.5, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:2, gen:10 IGP Id: 1.1.1.9, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:16 IGP Id: 1.1.1.14, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.33, nbr_node_id:8, gen:24 IGP Id: 1.1.1.17, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.3, nbr_node_id:10, gen:31 IGP Id: 1.1.1.21, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.4, nbr_node_id:15, gen:42 IGP Id: 1.1.1.25, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.11, nbr_node_id:1, gen:22 IGP Id: 1.1.1.29, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:2, gen:33 IGP Id: 1.1.1.33, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:40 IGP Id: 1.1.1.38, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:2, gen:19 IGP Id: 1.1.1.42, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:26 IGP Id: 1.1.1.46, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.22, nbr_node_id:6, gen:35 IGP Id: 1.1.1.49, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:2, gen:28 IGP Id: 1.1.1.53, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:37 PE1# |
| P1 |
|
P1#show mpls traffic-eng topology My_System_id: 10.255.255.1 (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) Signalling error holddown: 10 sec Global Link Generation 42
IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.1 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.2, nbr_node_id:3, gen:8 frag_id 8, Intf Address:1.1.1.1 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.2 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.5, nbr_node_id:5, gen:14 frag_id 8, Intf Address:1.1.1.6 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.3, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.3 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.25, nbr_node_id:11, gen:29 frag_id 10, Intf Address:1.1.1.26 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.4, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.4 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.17, nbr_node_id:16, gen:38 frag_id 8, Intf Address:1.1.1.18 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.11, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.11 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.2, nbr_node_id:3, gen:2 frag_id 11, Intf Address:1.1.1.2 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.22, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.22 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.9, nbr_node_id:7, gen:17 frag_id 11, Intf Address:1.1.1.10 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.33, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.33 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.38, nbr_node_id:9, gen:20 frag_id 13, Intf Address:1.1.1.37 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 10.255.255.44, MPLS TE Id:192.168.254.44 Router Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, DR: 1.1.1.33, nbr_node_id:21, gen:41 frag_id 13, Intf Address:1.1.1.34 TE metric:1, IGP metric:1, attribute flags:0x0 SRLGs: None physical_bw: 1000000 (kbps), max_reservable_bw_global: 750000 (kbps) max_reservable_bw_sub: 0 (kbps)
IGP Id: 1.1.1.2, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.11, nbr_node_id:2, gen:4 IGP Id: 1.1.1.5, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:1, gen:10 IGP Id: 1.1.1.9, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:16 IGP Id: 1.1.1.14, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.33, nbr_node_id:8, gen:24 IGP Id: 1.1.1.17, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.3, nbr_node_id:10, gen:31 IGP Id: 1.1.1.21, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.4, nbr_node_id:15, gen:42 IGP Id: 1.1.1.25, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.11, nbr_node_id:2, gen:22 IGP Id: 1.1.1.29, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:1, gen:33 IGP Id: 1.1.1.33, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:40 IGP Id: 1.1.1.38, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:1, gen:19 IGP Id: 1.1.1.42, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:26 IGP Id: 1.1.1.46, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.22, nbr_node_id:6, gen:35 IGP Id: 1.1.1.49, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.1, nbr_node_id:1, gen:28 IGP Id: 1.1.1.53, Network Node (ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0) link[0]: Broadcast, Nbr IGP Id: 10.255.255.2, nbr_node_id:4, gen:37 P1# |
Path Computation Configuration:
E’ il nodo headend che calcola il percorso per un LSP-TE.
Un tunnel interface definisce una destinazione per questo LSP-TE ed una lista di opzioni per raggiungere la destinazione prevista; queste opzioni si possono riferire in un modo esplicito per next-hop oppure in modo dinamico.
Anche se configuriamo un tunnel in modo esplicito, comunque un nodo LSR verifica il percorso usando il database TE (TED)
I comandi per la configurazione di un LSP-TE Path sono:
interface tunnel <number-tunnel >
dscription MPLS-TE-Tunnel
ip unnumbered Loopback10
tunnel destination < ipv4 destination-address >
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name < name-explicit-path >
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic
tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute
I comandi per la configurazione di un LSP-TE Path secondo Constraints sono:
tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth
tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity # utilizzato per includere/escludere un path
tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority # utilizzato per valori di priority su base setup ed holding
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-selection metric
E’ possibile anche l’utilizzo di un template attraverso il comando:
mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes (in global configuration)
Esempio
mpls traffic-eng lsp attribute LSP-constraint-x
affinity 0x0 mask 0xFFFFFFFF
bandwidth 50000
!
interface tunnel1
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic attributes LSP-constraint-x
Path Reoptimization Configuration:
Un nodo headend può reottimizzare in modo automatico un LSP-TE esistente in cerca di un percorso migliore
Il comando utilizzato è:
mpls traffic-eng reoptimize timers frequency: permette di stabilire un tempo di riottimizzazione del percorso
mpls traffic-eng reoptimize events link-up: permette di forzare una riottimizzazione del percorso a seguito di un evento come quando una interfaccia fisica diventa up
Il tempo di riottimizzazione di default = 1 ora
Ora andiamo a configurare la parte di Tunnel LSP di Traffic-Engineering nella rete di laboratorio:
1) visione architettura con attributi di default e relative tabelle di routing:
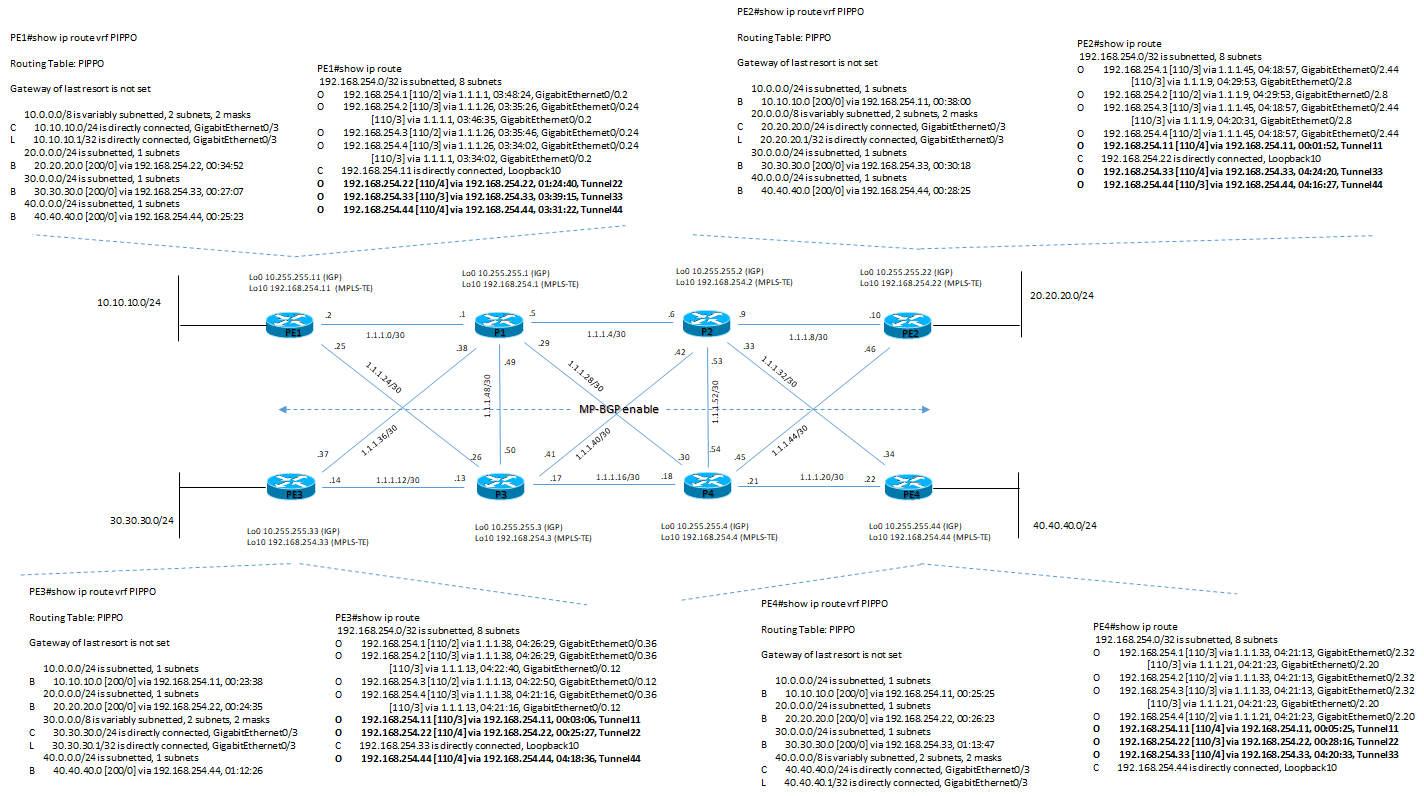
Configurazione Tunnel-TE:
|
PE1
|
PE2 |
|
interface Tunnel22 description to-pe2 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.22 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name path-lsp-explicit-pe2 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel33 description to-pe3 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.33 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel44 description to-pe4 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.44 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! ip explicit-path name path-lsp-explicit-pe2 enable next-address 1.1.1.1 next-address 1.1.1.6 next-address 1.1.1.10 ! |
interface Tunnel11 description to-pe1 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.11 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name path-lsp-explicit-pe1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel33 description to-pe3 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.33 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel44 description to-pe4 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.44 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! ip explicit-path name path-lsp-explicit-pe1 enable next-address 1.1.1.21 next-address 1.1.1.17 next-address 1.1.1.25 ! |
|
PE3
|
PE4 |
|
interface Tunnel11 description to-pe1 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.11 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel22 description to-pe2 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.22 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel44 description to-pe4 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.44 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! |
interface Tunnel11 description to-pe1 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.11 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel22 description to-pe2 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.22 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel33 description to-pe3 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.33 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! |
In condizioni di vincoli di default vediamo di analizzare il flusso di traffico rispettivamente:
1) sorgente 10.10.10.10 to destinazione 20.20.20.20 (LSP-TE)
L’architettura di riferimento è la seguente:
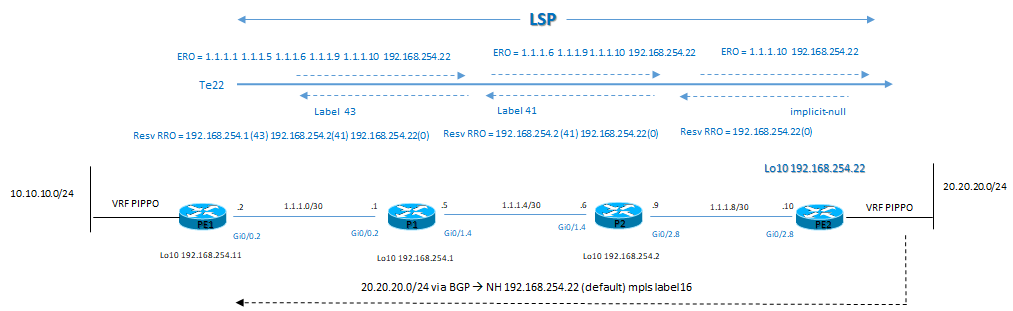
PC1> ping 20.20.20.20
84 bytes from 20.20.20.20 icmp_seq=1 ttl=60 time=34.920 ms
84 bytes from 20.20.20.20 icmp_seq=2 ttl=60 time=22.058 ms
84 bytes from 20.20.20.20 icmp_seq=3 ttl=60 time=21.069 ms
84 bytes from 20.20.20.20 icmp_seq=4 ttl=60 time=20.317 ms
84 bytes from 20.20.20.20 icmp_seq=5 ttl=60 time=22.449 ms
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20
trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop
1 10.10.10.1 2.474 ms 1.898 ms 2.121 ms
2 1.1.1.1 30.375 ms 23.469 ms 27.406 ms
3 1.1.1.6 24.796 ms 22.496 ms 27.554 ms
4 20.20.20.1 23.408 ms 22.577 ms 32.851 ms
5 *20.20.20.20 23.356 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PE2#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf PIPPO 20.20.20.0
BGP routing table entry for 65100:10:20.20.20.0/24, version 2
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table PIPPO)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
0.0.0.0 (via vrf PIPPO) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.254.22)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
Extended Community: RT:65100:10
mpls labels in/out 16/nolabel(PIPPO)
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
PE2#show ip route vrf PIPPO 20.20.20.0
Routing Table: PIPPO
Routing entry for 20.20.20.0/24
Known via “connected”, distance 0, metric 0 (connected, via interface)
Redistributing via bgp 65100
Advertised by bgp 65100
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* directly connected, via GigabitEthernet0/3
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
PE2#show mpls forwarding-table
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
16 No Label 20.20.20.0/24[V] 0 aggregate/PIPPO
PE1#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf PIPPO 20.20.20.0
BGP routing table entry for 65100:10:20.20.20.0/24, version 11
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table PIPPO)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
192.168.254.22 (metric 4) (via default) from 192.168.254.22 (192.168.254.22)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Extended Community: RT:65100:10
mpls labels in/out nolabel/16
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
PE1#show ip route vrf PIPPO 20.20.20.0
Routing Table: PIPPO
Routing entry for 20.20.20.0/24
Known via “bgp 65100”, distance 200, metric 0, type internal
Last update from 192.168.254.22 00:07:28 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.254.22 (default), from 192.168.254.22, 00:07:28 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 0
MPLS label: 16
MPLS Flags: MPLS Required
PE1#show ip route 192.168.254.22
Routing entry for 192.168.254.22/32
Known via “ospf 1”, distance 110, metric 4, type intra area
Last update from 192.168.254.22 on Tunnel22, 00:11:56 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.254.22, from 10.255.255.22, 00:11:56 ago, via Tunnel22
Route metric is 4, traffic share count is 1
PE1#show int tunnel 22
Tunnel22 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Tunnel
Description: to-pe2
Interface is unnumbered. Using address of Loopback10 (192.168.254.11)
MTU 17936 bytes, BW 100 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive not set
Tunnel linestate evaluation up
Tunnel source 192.168.254.11, destination 192.168.254.22
Tunnel protocol/transport Label Switching
Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Last input never, output 00:00:15, output hang never
Last clearing of “show interface” counters 00:26:39
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/0 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
36 packets output, 1970 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22
Name: to-pe2 (Tunnel22) Destination: 192.168.254.22
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe2 (Basis for Setup, path weight 3)
path option 20, type dynamic
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: explicit path option 10 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 43
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 141
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.2
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.9
1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.1(43) 192.168.254.2(41)
192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 3 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6
1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 53 minutes, 10 seconds
Time since path change: 39 minutes, 44 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 141
Current LSP:
Uptime: 39 minutes, 47 seconds
Selection: reoptimization
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 20 [140]
Removal Trigger: reoptimization completed
PE1#
P1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 43
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1.4, 41
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 141
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.5
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.2(41) 192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
P2#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1.4, 41
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/2.8, implicit-null
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 141
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.9
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Per quanto riguarda la parte di label mpls:
PE1#show mpls forwarding-table 192.168.254.22
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
41 [T] Pop Label 192.168.254.22/32
0 Tu22 point2point
[T] Forwarding through a LSP tunnel.
View additional labelling info with the ‘detail’ option
PE1#
PE1#show mpls forwarding-table 192.168.254.22 detail
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
41 Pop Label 192.168.254.22/32
0 Tu22 point2point
MAC/Encaps=18/22, MRU=1500, Label Stack{43}, via Gi0/0.2
0C8332DDD4000C8332E31700810000028847 0002B000
No output feature configured
P1#show mpls forwarding-table 192.168.254.22 detail
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
46 42 192.168.254.22/32
0 Gi0/1.4 1.1.1.6
MAC/Encaps=18/22, MRU=1500, Label Stack{42}
0C8332E489010C8332DDD401810000048847 0002A000
No output feature configured
Per-destination load-sharing, slots: 0
43 192.168.254.22/32
0 Gi0/1.28 1.1.1.30
MAC/Encaps=18/22, MRU=1500, Label Stack{43}
0C83328EF6010C8332DDD4018100001C8847 0002B000
No output feature configured
Per-destination load-sharing, slots: 1
P1#
P2#show mpls forwarding-table 192.168.254.22 detail
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
42 Pop Label 192.168.254.22/32
0 Gi0/2.8 1.1.1.10
MAC/Encaps=18/18, MRU=1504, Label Stack{}
0C83325F62020C8332E48902810000088847
No output feature configured
P2#
Vediamo ora gli aspetti di protezione dei tunnel-TE:
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22 protection
to-pe2
LSP Head, Tunnel22, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 141
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 43, nhop: 1.1.1.1
nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2
Path Protection: None
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels interface gi0/0.2 # vedi config sopra senza tunnel di backup
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels interface gi0/0.24
Name: to-pe3 (Tunnel33) Destination: 192.168.254.33
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 10, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 2)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 10 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 42
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.33, Tun_Id 33, Tun_Instance 63
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.25
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.13 1.1.1.14 192.168.254.33
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.3(42) 192.168.254.33(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 3 hours, 49 minutes
Time since path change: 48 minutes, 52 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 63
Current LSP:
Uptime: 48 minutes, 52 seconds
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 10 [32]
Removal Trigger: path error
Name: to-pe4 (Tunnel44) Destination: 192.168.254.44
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 20, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 3)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 20 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 45
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.44, Tun_Id 44, Tun_Instance 68
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.25
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.41 1.1.1.42 1.1.1.33
1.1.1.34 192.168.254.44
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.3(45) 192.168.254.2(45)
192.168.254.44(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 3 hours, 49 minutes
Time since path change: 48 minutes, 52 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 68
Current LSP:
Uptime: 48 minutes, 52 seconds
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 20 [55]
Removal Trigger: path error
LSP Tunnel to-pe1 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.22, Dst 192.168.254.11, Tun_Id 11, Tun_Instance 60
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.11
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
LSP Tunnel to-pe1 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.33, Dst 192.168.254.11, Tun_Id 11, Tun_Instance 35
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.11
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
LSP Tunnel to-pe1 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.44, Dst 192.168.254.11, Tun_Id 11, Tun_Instance 21
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.11
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
PE1#
P1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels protection
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 43
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1.4, 41
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 141
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.5
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.2(41) 192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
P2#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels protection
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1.4, 41
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/2.8, implicit-null
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 141
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.9
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
PE2#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels protection
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/2.8, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 141
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.22
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Simuliamo il fault dell’interface gi0/0.2 del PE1 con ip address 1.1.1.2/30
PE1(config)#int gi0/0.2
PE1(config-subif)#shutdown
PE1(config-subif)#
*May 2 15:56:51.631: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.1 on GigabitEthernet0/0.2 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
*May 2 15:56:51.648: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_141: DOWN: path error
*May 2 15:56:51.657: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_32: DOWN: path error
*May 2 15:56:51.667: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_55: DOWN: path error
*May 2 15:56:51.680: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.1:0 (1) is DOWN (Interface not operational)
*May 2 15:56:51.781: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_35: UP
*May 2 15:56:51.831: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_63: UPe
PE1(config-subif)#exit
*May 2 15:56:51.841: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_21: UP
*May 2 15:56:51.851: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_144: UP
*May 2 15:56:51.891: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_68: UP
PE1(config-subif)#exit
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22
Name: to-pe2 (Tunnel22) Destination: 192.168.254.22
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 20, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 3)
path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe2
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 20 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 43
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 144
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.25
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.41 1.1.1.42 1.1.1.9
1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.3(43) 192.168.254.2(44)
192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 3 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.25 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.41 1.1.1.42
1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 3 hours, 5 minutes
Time since path change: 5 minutes, 21 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 144
Current LSP:
Uptime: 5 minutes, 21 seconds
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 10 [141]
Removal Trigger: path error
Last Error: PCALC:: No addresses to connect 192.168.254.11 to 1.1.1.1
PE1#
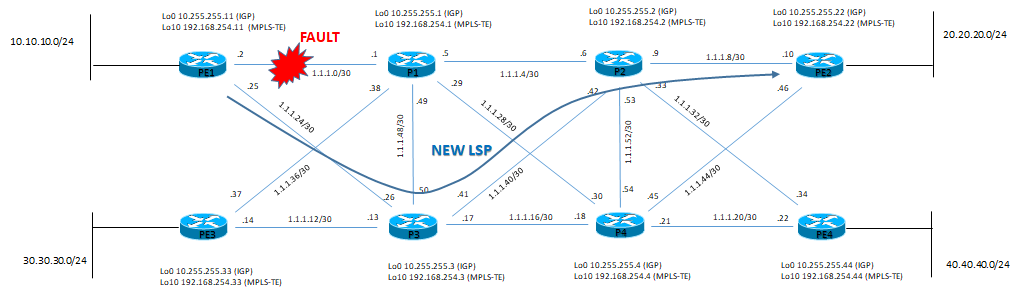
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20
trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop
1 10.10.10.1 2.665 ms 1.614 ms 1.916 ms
2 1.1.1.26 22.030 ms 20.096 ms 16.889 ms
3 1.1.1.42 19.159 ms 21.689 ms 22.976 ms
4 20.20.20.1 21.949 ms 26.663 ms 23.502 ms
5 * * *
6 *20.20.20.20 23.907 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
Lato P-router abbiamo ovviamente la seguente situazione:
P1#
*May 2 15:56:52.549: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.11:0 (1) is DOWN (Received error notification from peer: Holddown time expired)
P1#
*May 2 15:56:58.689: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_6: DOWN
*May 2 15:56:58.772: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_10: DOWN
P1#
*May 2 15:57:19.527: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.11 on GigabitEthernet0/0.2 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
P1#
*May 2 15:59:52.475: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_32: DOWN
P1#
*May 2 16:00:00.525: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_141: DOWN
P1#
*May 2 16:00:06.786: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_55: DOWN
P1#
PE2#
*May 2 15:57:02.599: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_144: UP
PE2#
*May 2 16:00:17.730: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_141: DOWN
PE2#
P3#
*May 2 13:09:40.952: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_60: UP
*May 2 13:09:40.974: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_30: UP
P3#
*May 2 15:56:56.903: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_35: UP
*May 2 15:56:56.914: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_63: UP
*May 2 15:56:56.940: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_144: UP
*May 2 15:56:56.976: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_21: UP
*May 2 15:56:56.993: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_68: UP
P3#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 43
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1.40, 44
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 144
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.41
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.42 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.2(44) 192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
P2#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels
LSP Tunnel to-pe2 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1.40, 44
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/2.8, implicit-null
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 144
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.9
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
L’output from PE1 cambia l’interface di out e ìd il next-hop:
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22 protection
to-pe2
LSP Head, Tunnel22, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 144
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 43, nhop: 1.1.1.26
nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2
Path Protection: None
Proviamo ora a costruire un progetto di rete sulla nostra rete di laboratorio:
Assunzioni:
Un Tunnel-IT è sempre unidirezionale (nella architettura GMPLS possiamo trovare tunnel bidirezionali)
Per flusso di traffico in genere si intende un aggregato che appartiene alla stessa classe di servizio ed è definito da parametri quali:
< ip_sorgente ; ip_destinazione ; protocollo_ID ; porta_tcp-udp_sorgente ; porta tcp-udp_destinazione >
Gli attributi per un flusso di traffico possono essere:
parametri quali bandwidth, metric e possibilità di allocazione di banda sulla base di azione di verifica da intraprendere (policing) e controllo di accettazione del traffico
selezione e gestione dei percorsi che possono essere di tipo:
automatico tramite algoritmi di instradamento a volte soggetti a determinati vincoli (constraint) di inclusione/esclusione di link o di banda
manuale e quindi gestiti da un operatore sulla base delle caratteristiche che la rete presenta e possono essere di tipo strict (definizione di tutt i nodi di un LSP) oppure loose (definizione parziale dei nodi di un LSP ed in questo ultimo caso sono gli algoritmi di instradamento a completare il percorso)
priorità su base setup ed holding
modalità di recupero si riferisce alla resilienza della rete nella capacità di reinstradamento o meno attraverso percorsi alternativi di un flusso di traffico
In genere un nodo head-end ragione per la costruzione di un patch LSP come in figura:
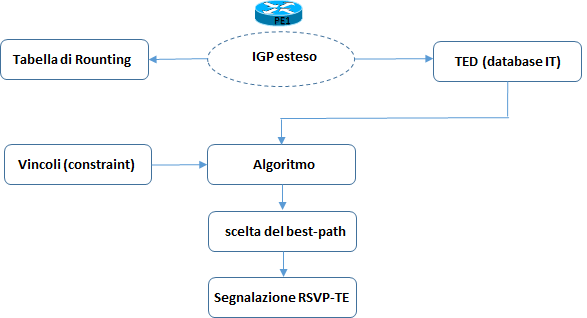
Un TED si costruisce attraverso un protocollo IGP di tipo link-state opportunamente estesi per il trasporto delle informazioni per topologia di rete, attributi associati ai link e classi amministrative di appartenenza.
Le informazioni, quindi, distribuite possono essere la banda residua disponibile, i colori di inclusione/esclusione, le metriche IT (in genere la metrica IT coincide con quella IGP)
Le informazioni sono trasportate attraverso LSA type 10 opaque per OSPF e sub-TLV per ISIS ed in genere attraversano una sola area di dominio (ovviamente è possibile avere LSP in contesti multi-area oppure multi-AS) ed in generale utilizzano questi campi:
- Router address (TLV=1): è l’indirizzo IP address del router che invia le informazioni IT
- Link (TLV=2): definisce circa 9 oggetti e sono:
- – link type (1 byte): definisce il tipo di collegamento P2P oppure multiaccess ad esempio ethernet
- – link ID (4 byte): identifica il punto remoto del collegamento di tipo P2P oppure l’identificatico del router adiacente che nel caso di OSPF in una rete multiaccess è il designated router
- – local interface IP address (4 byte): indica l’indirizzo IP della interfaccia di collegamento
- – remote interface IP address (4 byte): indica l’indirizzo IP della interfaccia del router remoto del collegamento
- – metric-TE (4 byte): contiene il valore di metrica IT
- – Maximum Bandwidth (4 byte): indica la massima banda disponibile per tunnel-IT di un collegamento
- – Unreserved Bandwidth (32 byte): indica per ciascuno degli otto livelli di priorità (da 0 a 7) la banda per tunnel-IT disponibile sul collegamento (banda residua); i valori iniziali sono posti come Maximim Reservable BW
- – Administrative Group (4 byte): contiene la maschera di appartenza alle classi amministrative definite come vettori booleani di proprietà)
Gli Algoritmi per la selezione di un percorso possono essere di tipo off-line con sofisticate funzioni matematiche oppure on-line che sono più facilmente utilizzabili e tra i principali abbiamo:
CSPF (Constrained Shortest Path First – Djikstra) e si basa principalmente sul binomio < metrica IT ; banda residua disponibile >
SWP (Shortest-Widest Path) e si basa per la selezione in modo sequenziale a < metrica IT minima > < path con numero minore di hop > < percorso random >
Ibrido e si basa su un mix dei vantaggi dei primi due e si basa su una metrica dei link che penalizzi la lunghezza eccessiva del percorso ed anche la banda minima residua disponibile
Definizione parametri di progetto:
Configurazione tunnel primari e di backup from PE1
|
PE1 configurazione Tunnel-TE |
PE1 explicit-path |
|
interface Tunnel22 description to-pe2 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.22 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name path-lsp-explicit-pe2 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel33 description to-pe3 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.33 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name path-lsp-explicit-pe3 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel44 description to-pe4 ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.44 tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name path-lsp-explicit-pe4 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute ! interface Tunnel222 description to-pe2-backup ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.22 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name lsp-backup-22 ! interface Tunnel333 description to-pe3-backup ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.33 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name lsp-backup-33 ! interface Tunnel444 description tp-pe4-backup ip unnumbered Loopback10 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination 192.168.254.44 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name lsp-backup-44 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 description to-P1 encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng backup-path Tunnel333 mpls traffic-eng backup-path Tunnel444 mpls ip ip rsvp bandwidth ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.24 description to-P3 encapsulation dot1Q 24 ip address 1.1.1.25 255.255.255.252 ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng backup-path Tunnel222 mpls ip ip rsvp bandwidth |
ip explicit-path name path-lsp-explicit-pe2 enable next-address 1.1.1.1 next-address 1.1.1.6 next-address 1.1.1.10 ! ip explicit-path name path-lsp-explicit-pe3 enable next-address 1.1.1.26 next-address 1.1.1.14 ! ip explicit-path name path-lsp-explicit-pe4 enable next-address 1.1.1.26 next-address 1.1.1.42 next-address 1.1.1.54 next-address 1.1.1.22 ! ip explicit-path name lsp-backup-22 enable exclude-address 1.1.1.1 ! ip explicit-path name lsp-backup-33 enable index 2 exclude-address 1.1.1.26 ! ip explicit-path name lsp-backup-44 enable exclude-address 1.1.1.26 ! |
Verifica configurazione tunnel UP
PE1#show ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.2 1.1.1.2 YES NVRAM up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.24 1.1.1.25 YES NVRAM up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/3 10.10.10.1 YES NVRAM up up
Loopback0 10.255.255.11 YES NVRAM up up
Loopback10 192.168.254.11 YES NVRAM up up
Tunnel22 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel33 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel44 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel222 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel333 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel444 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
| verifica tunnel primario TE22 | verifica tunnel backup TE222 |
|
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22 Name: to-pe2 (Tunnel22) Destination: 192.168.254.22 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe2 (Basis for Setup, path weight 3) path option 20, type dynamic Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled Active Path Option Parameters: State: explicit path option 10 is active BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled InLabel : – OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 26 RSVP Signalling Info: Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 69 RSVP Path Info: My Address: 1.1.1.2 Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22 Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: 192.168.254.1(26) 192.168.254.2(24) 192.168.254.22(0) Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits Shortest Unconstrained Path Info: Path Weight: 3 (TE) Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22 History: Tunnel: Time since created: 3 hours, 6 minutes Time since path change: 2 hours, 57 minutes Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 69 Current LSP: Uptime: 2 hours, 57 minutes |
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 222 Name: to-pe2-backup (Tunnel222) Destination: 192.168.254.22 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 10, type explicit lsp-backup-22 (Basis for Setup, path weight 3) Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled Active Path Option Parameters: State: explicit path option 10 is active BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled InLabel : – OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 39 RSVP Signalling Info: Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 222, Tun_Instance 3 RSVP Path Info: My Address: 1.1.1.25 Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.41 1.1.1.42 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22 Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits Shortest Unconstrained Path Info: Path Weight: 3 (TE) Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.9 1.1.1.10 192.168.254.22 History: Tunnel: Time since created: 25 minutes, 33 seconds Time since path change: 20 minutes, 15 seconds Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 3 Current LSP: Uptime: 20 minutes, 15 seconds PE1# |
|
Verifica Tunnel primario TE33
|
Verfiica Tunnel backup TE333 |
|
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 33 Name: to-pe3 (Tunnel33) Destination: 192.168.254.33 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe3 (Basis for Setup, path weight 2) path option 20, type dynamic Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled Active Path Option Parameters: State: explicit path option 10 is active BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled InLabel : – OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 40 FRR OutLabel : Tunnel333, explicit-null RSVP Signalling Info: Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.33, Tun_Id 33, Tun_Instance 70 RSVP Path Info: My Address: 1.1.1.25 Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.13 1.1.1.14 192.168.254.33 Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: 192.168.254.3(40) 192.168.254.33(0) Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits Shortest Unconstrained Path Info: Path Weight: 2 (TE) Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.37 192.168.254.33 History: Tunnel: Time since created: 3 hours, 15 minutes Time since path change: 15 minutes, 18 seconds Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 70 Current LSP: Uptime: 15 minutes, 21 seconds Selection: reoptimization Prior LSP: ID: path option 20 [69] Removal Trigger: reoptimization completed PE1#
|
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 333 Name: to-pe3-backup (Tunnel333) Destination: 192.168.254.33 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 10, type explicit lsp-backup-33 (Basis for Setup, path weight 2) Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled Active Path Option Parameters: State: explicit path option 10 is active BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled InLabel : – OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 53 RSVP Signalling Info: Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.33, Tun_Id 333, Tun_Instance 5 RSVP Path Info: My Address: 1.1.1.2 Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.37 192.168.254.33 Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits Shortest Unconstrained Path Info: Path Weight: 2 (TE) Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.37 192.168.254.33 History: Tunnel: Time since created: 32 minutes, 3 seconds Time since path change: 24 minutes, 55 seconds Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 5 Current LSP: Uptime: 24 minutes, 55 seconds Selection: reoptimization Prior LSP: ID: path option 10 [4] Removal Trigger: configuration changed PE1# |
|
Verifica tunnel primario TE44
|
Verifica tunnel backup TE444 |
|
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 44 Name: to-pe4 (Tunnel44) Destination: 192.168.254.44 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe4 (Basis for Setup, path weight 4) path option 20, type dynamic Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled Active Path Option Parameters: State: explicit path option 10 is active BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled InLabel : – OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 41 RSVP Signalling Info: Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.44, Tun_Id 44, Tun_Instance 89 RSVP Path Info: My Address: 1.1.1.25 Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.41 1.1.1.42 1.1.1.53 1.1.1.54 1.1.1.21 1.1.1.22 192.168.254.44 Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: 192.168.254.3(41) 192.168.254.2(51) 192.168.254.4(39) 192.168.254.44(0) Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits Shortest Unconstrained Path Info: Path Weight: 3 (TE) Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.33 1.1.1.34 192.168.254.44 History: Tunnel: Time since created: 3 hours, 20 minutes Time since path change: 20 minutes, 18 seconds Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 89 Current LSP: Uptime: 20 minutes, 21 seconds Selection: reoptimization Prior LSP: ID: path option 20 [83] Removal Trigger: reoptimization completed PE1# |
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 444 Name: tp-pe4-backup (Tunnel444) Destination: 192.168.254.44 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 10, type explicit lsp-backup-44 (Basis for Setup, path weight 3) Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled Active Path Option Parameters: State: explicit path option 10 is active BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled InLabel : – OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 51 RSVP Signalling Info: Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.44, Tun_Id 444, Tun_Instance 2 RSVP Path Info: My Address: 1.1.1.2 Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.33 1.1.1.34 192.168.254.44 Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits Shortest Unconstrained Path Info: Path Weight: 3 (TE) Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.5 1.1.1.6 1.1.1.33 1.1.1.34 192.168.254.44 History: Tunnel: Time since created: 35 minutes, 39 seconds Time since path change: 32 minutes, 57 seconds Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 2 Current LSP: Uptime: 32 minutes, 57 seconds PE1# |
Verifica percorsi espliciti primari from PC1 e dal PE1
|
From PC1
|
From PE1 |
|
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20 trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.394 ms 1.962 ms 1.804 ms 2 1.1.1.1 22.358 ms 20.580 ms 16.219 ms 3 1.1.1.6 23.198 ms 28.622 ms 24.804 ms 4 20.20.20.1 22.253 ms 24.283 ms 22.536 ms 5 *20.20.20.20 26.148 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 30.30.30.30 trace to 30.30.30.30, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 12.118 ms 3.767 ms 2.538 ms 2 1.1.1.26 16.254 ms 16.567 ms 15.386 ms 3 30.30.30.1 18.732 ms 15.956 ms 17.835 ms 4 *30.30.30.30 16.828 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40 trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.977 ms 1.954 ms 1.972 ms 2 1.1.1.26 24.449 ms 28.769 ms 24.418 ms 3 1.1.1.42 26.328 ms 23.712 ms 27.232 ms 4 1.1.1.54 24.406 ms 30.054 ms 21.071 ms 5 40.40.40.1 33.779 ms 31.866 ms 24.027 ms 6 *40.40.40.40 30.161 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) |
PE1#traceroute vrf PIPPO 20.20.20.20 source 10.10.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 20.20.20.20 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 1.1.1.1 [MPLS: Labels 26/30 Exp 0] 26 msec 24 msec 29 msec 2 1.1.1.6 [MPLS: Labels 24/30 Exp 0] 24 msec 26 msec 17 msec 3 20.20.20.1 28 msec 29 msec 23 msec 4 20.20.20.20 29 msec 25 msec 26 msec
PE1#traceroute vrf PIPPO 30.30.30.30 source 10.10.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 30.30.30.30 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 1.1.1.26 [MPLS: Labels 40/37 Exp 0] 19 msec 15 msec 15 msec 2 30.30.30.1 18 msec 21 msec 15 msec 3 30.30.30.30 3000 msec 16 msec 13 msec PE1#
PE1#traceroute vrf PIPPO 40.40.40.40 source 10.10.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 40.40.40.40 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 1.1.1.26 [MPLS: Labels 41/16 Exp 0] 30 msec 27 msec 31 msec 2 1.1.1.42 [MPLS: Labels 51/16 Exp 0] 23 msec 28 msec 22 msec 3 1.1.1.54 [MPLS: Labels 39/16 Exp 0] 25 msec 19 msec 31 msec 4 40.40.40.1 29 msec 26 msec 29 msec 5 40.40.40.40 2999 msec 28 msec 27 msec |
I percorsi sono quelli esplicitati.
Ora andiamo a testare la funzionalità dei tunnel di backup:
1) FAULT LINK PE1 gi0/0.24
PE1(config)#int gi0/0.24
PE1(config-subif)#shut
PE1(config-subif)#shutdown
PE1(config-subif)#
*May 3 10:41:20.149: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.3 on GigabitEthernet0/0.24 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
*May 3 10:41:20.158: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_70: DOWN: path error
*May 3 10:41:20.166: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_89: DOWN: path error
*May 3 10:41:20.171: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 222_3: DOWN: path error
*May 3 10:41:20.181: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.3:0 (2) is DOWN (Interface not operational)
*May 3 10:41:20.303: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_72: UP
*May 3 10:41:20.350: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_91: UP
PE1#
*May 3 10:41:35.344: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Tunnel222, changed state to down
PE1#
PE1#show ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.2 1.1.1.2 YES NVRAM up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.23 unassigned YES unset up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.24 1.1.1.25 YES NVRAM administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/3 10.10.10.1 YES NVRAM up up
Loopback0 10.255.255.11 YES NVRAM up up
Loopback10 192.168.254.11 YES NVRAM up up
Tunnel22 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel33 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel44 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel222 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up down
Tunnel333 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel444 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Verifica path con differenza tra prima e dopo il fault con punto di vista del PC1
|
PC1 verifica path prima del FAULT LINK
|
PC1 verifica path dopo il FAULT-LINK |
|
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20 trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.394 ms 1.962 ms 1.804 ms 2 1.1.1.1 22.358 ms 20.580 ms 16.219 ms 3 1.1.1.6 23.198 ms 28.622 ms 24.804 ms 4 20.20.20.1 22.253 ms 24.283 ms 22.536 ms 5 *20.20.20.20 26.148 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 30.30.30.30 trace to 30.30.30.30, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 12.118 ms 3.767 ms 2.538 ms 2 1.1.1.26 16.254 ms 16.567 ms 15.386 ms 3 30.30.30.1 18.732 ms 15.956 ms 17.835 ms 4 *30.30.30.30 16.828 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40 trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.977 ms 1.954 ms 1.972 ms 2 1.1.1.26 24.449 ms 28.769 ms 24.418 ms 3 1.1.1.42 26.328 ms 23.712 ms 27.232 ms 4 1.1.1.54 24.406 ms 30.054 ms 21.071 ms 5 40.40.40.1 33.779 ms 31.866 ms 24.027 ms 6 *40.40.40.40 30.161 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) |
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20 trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.789 ms 1.865 ms 1.950 ms 2 1.1.1.1 25.508 ms 20.879 ms 19.449 ms 3 1.1.1.6 23.816 ms 25.025 ms 24.263 ms 4 20.20.20.1 24.729 ms 21.746 ms 27.313 ms 5 * * * 6 *20.20.20.20 23.890 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 30.30.30.30 trace to 30.30.30.30, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 2.659 ms 1.476 ms 2.875 ms 2 1.1.1.1 22.171 ms 16.137 ms 19.086 ms 3 30.30.30.1 15.569 ms 16.130 ms 19.969 ms 4 * * * 5 *30.30.30.30 15.368 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40 trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 2.479 ms 2.074 ms 1.940 ms 2 1.1.1.1 25.591 ms 21.854 ms 25.144 ms 3 1.1.1.6 23.920 ms 26.935 ms 21.023 ms 4 40.40.40.1 20.044 ms 19.498 ms 24.661 ms 5 * * * 6 *40.40.40.40 27.975 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) |
Appena si ripristina il Fault:
PE1(config)#int gi0/0.24
PE1(config-subif)#no shut
PE1(config-subif)#
*May 3 10:55:00.790: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.3:0 (2) is UP
PE1(config-subif)#
*May 3 10:55:05.400: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.3 on GigabitEthernet0/0.24 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done
*May 3 10:55:06.063: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 33_79: UP
*May 3 10:55:06.076: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 222_41: UP
*May 3 10:55:06.077: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Tunnel222, changed state to up
*May 3 10:55:06.142: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_98: UP
PE1(config-subif)#
e magicamente tutto torna come prima:
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40
trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop
1 10.10.10.1 1.660 ms 1.893 ms 1.949 ms
2 1.1.1.26 24.876 ms 32.364 ms 21.915 ms
3 1.1.1.42 28.907 ms 22.272 ms 25.136 ms
4 1.1.1.54 27.071 ms 28.954 ms 22.998 ms
5 40.40.40.1 29.121 ms 23.410 ms 22.032 ms
6 * * *
7 *40.40.40.40 13.573 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
E’ interessante notare il comando mpls traffic-eng tunnel protection prima e dopo il fault del link
|
PE1 show mpls traffic-eng tunnel protection prima del fault link |
PE1 show mpls traffic-eng tunnel protection dopo il fault link |
| PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels protection
to-pe2 LSP Head, Tunnel22, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 69 Fast Reroute Protection: Requested Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned LSP signalling info: Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 26, nhop: 1.1.1.1 nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2 Path Protection: None
to-pe3 LSP Head, Tunnel33, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 79 Fast Reroute Protection: Requested Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned LSP signalling info: Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 39, nhop: 1.1.1.26 nnhop: 192.168.254.33; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.33 Path Protection: None
to-pe4 LSP Head, Tunnel44, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 98 Fast Reroute Protection: Requested Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned LSP signalling info: Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 41, nhop: 1.1.1.26 nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2 Path Protection: None
to-pe2-backup LSP Head, Tunnel222, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 41 Fast Reroute Protection: None Path Protection: None
to-pe3-backup LSP Head, Tunnel333, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 5 Fast Reroute Protection: None Path Protection: None
to-pe4-backup LSP Head, Tunnel444, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 2 Fast Reroute Protection: None Path Protection: None |
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels protection to-pe2 LSP Head, Tunnel22, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 69 Fast Reroute Protection: Requested Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned LSP signalling info: Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 26, nhop: 1.1.1.1 nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2 Path Protection: None
to-pe3 LSP Head, Tunnel33, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 72 Fast Reroute Protection: Requested Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned LSP signalling info: Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 31, nhop: 1.1.1.1 nnhop: 192.168.254.33; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.33 Path Protection: None
to-pe4 LSP Head, Tunnel44, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 91 Fast Reroute Protection: Requested Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned LSP signalling info: Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 52, nhop: 1.1.1.1 nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2 Path Protection: None
to-pe2-backup LSP Head, Tunnel222, Admin: up, Oper: down Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 0 Fast Reroute Protection: None Path Protection: Backup lsp in use.
to-pe3-backup LSP Head, Tunnel333, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 5 Fast Reroute Protection: None Path Protection: None
to-pe4-backup LSP Head, Tunnel444, Admin: up, Oper: up Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 2 Fast Reroute Protection: None Path Protection: None |
Vediamo cosa succede se il fault è provocato lato P-router (nel nostro esempio da P1)
P1(config)#int gi0/0.2
P1(config-subif)#shut
P1(config-subif)#
*May 3 12:45:24.635: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.11 on GigabitEthernet0/0.2 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
*May 3 12:45:24.642: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 333_31: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.648: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_59: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.656: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.11:0 (1) is DOWN (Interface not operational)
*May 3 12:45:24.741: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_8: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.790: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_12: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.805: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_18: DOWN
P1(config-subif)#exit
P1(config)#exit
PE1#
*May 3 12:45:27.228: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 333_31: DOWN: path verification failed
*May 3 12:45:27.253: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_59: DOWN: path verification failed
*May 3 12:45:27.277: %BFD-6-BFD_SESS_DESTROYED: BFD-SYSLOG: bfd_session_destroyed, handle:1 neigh proc:FRR, handle:1 act
PE1#
*May 3 12:45:27.295: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_31: UP
*May 3 12:45:27.302: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_16: UP
*May 3 12:45:27.306: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_70: UP
*May 3 12:45:27.440: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_51: UP
PE1#
*May 3 12:45:35.155: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.1:0 (1) is DOWN (Received error notification from peer: Holddown time expired)
PE1#
*May 3 12:45:42.273: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Tunnel333, changed state to down
*May 3 12:45:42.279: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Tunnel444, changed state to down
PE1#
*May 3 12:45:58.805: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.1 on GigabitEthernet0/0.2 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
PE1#
PE1#show ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.2 1.1.1.2 YES NVRAM up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.23 unassigned YES unset up up
GigabitEthernet0/0.24 1.1.1.25 YES NVRAM up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/3 10.10.10.1 YES NVRAM up up
Loopback0 10.255.255.11 YES NVRAM up up
Loopback10 192.168.254.11 YES NVRAM up up
Tunnel22 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel33 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel44 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel222 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up up
Tunnel333 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up down
Tunnel444 192.168.254.11 YES TFTP up down
Anche tutti gli altri nodi P-router via segnalazione si accorgono del fault link from P1:
P2#
*May 3 12:45:24.345: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_59: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.375: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_12: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.391: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_18: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:24.499: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_16: UP
*May 3 12:45:24.502: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_70: UP
*May 3 12:45:24.530: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_51: UP
P3#
*May 3 12:45:26.528: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_31: UP
*May 3 12:45:26.531: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_16: UP
*May 3 12:45:26.534: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_70: UP
*May 3 12:45:26.620: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_51: UP
P3#
E lo stesso from PE router:
PE2#
*May 3 12:45:27.361: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_18: DOWN: path error
*May 3 12:45:27.510: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_51: UP
*May 3 12:45:27.530: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_70: UP
PE2#
*May 3 12:48:44.807: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_49: DOWN
PE3#
*May 3 12:45:27.725: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 333_31: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:27.734: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_8: DOWN: path error
*May 3 12:45:27.886: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 11_31: UP
PE4#
*May 3 12:45:30.208: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_12: DOWN: path error
*May 3 12:45:30.239: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_59: DOWN
*May 3 12:45:30.374: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_16: UP
Questo ricalcolo di path di LSP porta al risultato medesimo a prima:
|
From PC1 prima del fault Link
|
From PC1 dopo il fault Link |
|
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20 trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.394 ms 1.962 ms 1.804 ms 2 1.1.1.1 22.358 ms 20.580 ms 16.219 ms 3 1.1.1.6 23.198 ms 28.622 ms 24.804 ms 4 20.20.20.1 22.253 ms 24.283 ms 22.536 ms 5 *20.20.20.20 26.148 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 30.30.30.30 trace to 30.30.30.30, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 12.118 ms 3.767 ms 2.538 ms 2 1.1.1.26 16.254 ms 16.567 ms 15.386 ms 3 30.30.30.1 18.732 ms 15.956 ms 17.835 ms 4 *30.30.30.30 16.828 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40 trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 1.977 ms 1.954 ms 1.972 ms 2 1.1.1.26 24.449 ms 28.769 ms 24.418 ms 3 1.1.1.42 26.328 ms 23.712 ms 27.232 ms 4 1.1.1.54 24.406 ms 30.054 ms 21.071 ms 5 40.40.40.1 33.779 ms 31.866 ms 24.027 ms 6 *40.40.40.40 30.161 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) |
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20 trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 2.249 ms 2.214 ms 1.626 ms 2 1.1.1.26 30.065 ms 27.569 ms 25.093 ms 3 1.1.1.42 22.284 ms 25.062 ms 37.222 ms 4 20.20.20.1 32.476 ms 24.993 ms 21.344 ms 5 * * * 6 *20.20.20.20 25.755 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 30.30.30.30 trace to 30.30.30.30, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 2.305 ms 2.082 ms 2.164 ms 2 1.1.1.26 12.575 ms 16.012 ms 16.154 ms 3 30.30.30.1 13.718 ms 19.640 ms 13.097 ms 4 * * * 5 *30.30.30.30 15.976 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40 trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.10.10.1 2.052 ms 1.948 ms 2.260 ms 2 1.1.1.26 32.009 ms 26.950 ms 26.055 ms 3 1.1.1.42 27.868 ms 25.533 ms 24.671 ms 4 1.1.1.54 25.812 ms 22.320 ms 25.292 ms 5 40.40.40.1 23.423 ms 23.953 ms 20.896 ms 6 * * * 7 *40.40.40.40 21.707 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) |
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels protection
to-pe2
LSP Head, Tunnel22, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 51
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 45, nhop: 1.1.1.26
nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2
Path Protection: None
to-pe3
LSP Head, Tunnel33, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 75
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 35, nhop: 1.1.1.26
nnhop: 192.168.254.33; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.33
Path Protection: None
to-pe4
LSP Head, Tunnel44, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 123
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 41, nhop: 1.1.1.26
nnhop: 192.168.254.2; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.2
Path Protection: None
to-pe2-backup
LSP Head, Tunnel222, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 38
Fast Reroute Protection: None
Path Protection: None
to-pe3-backup
LSP Head, Tunnel333, Admin: up, Oper: down
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 0
Fast Reroute Protection: None
Path Protection: Backup lsp in use.
to-pe4-backup
LSP Head, Tunnel444, Admin: up, Oper: down
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 0
Fast Reroute Protection: None
Path Protection: Backup lsp in use.
LSP Tunnel to-pe1 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.22, Dst 192.168.254.11, Tun_Id 11, Tun_Instance 70
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.11
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
LSP Tunnel to-pe1 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.33, Dst 192.168.254.11, Tun_Id 11, Tun_Instance 31
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.11
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
LSP Tunnel to-pe1 is signalled, connection is up
InLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, implicit-null
OutLabel : –
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.44, Dst 192.168.254.11, Tun_Id 11, Tun_Instance 16
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.254.11
Explicit Route: NONE
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
PE1#
Vediamo ora cosa succede se abbiamo un fault a livello di nodo core P-router (P2 nel nostro esempio)
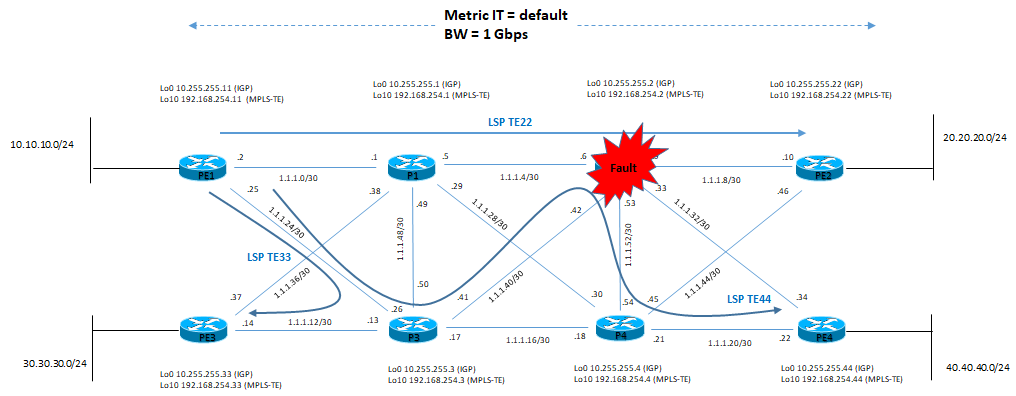
P1#
*May 3 13:29:49.895: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.2:0 (3) is DOWN (Discovery Hello Hold Timer expired)
P1#
*May 3 13:30:08.425: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_23: UP
P1#
*May 3 13:30:12.940: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.2 on GigabitEthernet0/1.4 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
*May 3 13:30:12.946: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_11: DOWN
*May 3 13:30:13.045: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_46: UP
*May 3 13:30:13.088: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_13: UP
P1#
*May 3 13:30:14.439: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_23: UP
P1#
*May 3 13:30:21.389: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_21: DOWN
P3#
*May 3 13:29:06.430: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.2:0 (1) is DOWN (Discovery Hello Hold Timer expired)
*May 3 13:29:25.732: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_54: UP
*May 3 13:29:25.742: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_129: UP
*May 3 13:29:25.844: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 22_47: UP
*May 3 13:29:31.681: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.2 on GigabitEthernet0/1.40 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
*May 3 13:29:31.803: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 33_34: UP
*May 3 13:29:31.813: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 44_58: UP
*May 3 13:29:38.868: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 22_32: DOWN
*May 3 13:29:44.794: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_21: DOWN
*May 3 13:29:44.878: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 44_41: DOWN
P3#
*May 3 13:32:09.353: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 33_17: DOWN
*May 3 13:32:09.369: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_39: DOWN
P3#
P4#
*May 3 13:29:11.241: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.2:0 (2) is DOWN (Discovery Hello Hold Timer expired)
P4#
*May 3 13:29:28.997: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 22_33: UP
*May 3 13:29:29.003: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 44_64: UP
*May 3 13:29:29.060: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_54: UP
*May 3 13:29:29.081: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_129: UP
*May 3 13:29:29.105: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_23: UP
*May 3 13:29:29.127: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 22_47: UP
P4#
*May 3 13:29:33.763: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_46: UP
*May 3 13:29:33.777: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_13: UP
P4#
*May 3 13:29:35.120: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 44_58: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.129: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_23: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.164: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 33_34: UP
P4#
*May 3 13:29:36.536: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.2 on GigabitEthernet0/3 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
P4#
*May 3 13:32:17.659: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_21: DOWN
E lato PE router:
PE1#
*May 3 13:30:12.023: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_129: UP
*May 3 13:30:12.139: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_23: UP
PE1#
*May 3 13:30:16.694: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_11: DOWN: path error
*May 3 13:30:16.718: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_46: UP
*May 3 13:30:16.783: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_13: UP
PE1#
*May 3 13:30:18.132: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_23: UP
PE1#
*May 3 13:33:30.845: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_43: DOWN
*May 3 13:33:30.850: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_125: DOWN
PE2#
*May 3 13:29:18.920: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.2:0 (1) is DOWN (Discovery Hello Hold Timer expired)
PE2#
*May 3 13:29:34.923: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.2 on GigabitEthernet0/2.8 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
*May 3 13:29:35.004: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 22_33: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.051: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 44_64: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.113: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_54: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.117: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_23: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.133: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 11_129: UP
*May 3 13:29:35.138: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 22_47: UP
PE2#
*May 3 13:32:45.657: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 22_12: DOWN
*May 3 13:32:45.838: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 22_32: DOWN
PE2#
*May 3 13:32:52.784: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 22_21: DOWN
PE2#
PE3#
*May 3 13:29:32.289: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_54: UP
*May 3 13:29:32.432: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 22_47: UP
PE3#
*May 3 13:29:38.387: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 33_34: UP
*May 3 13:29:38.443: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 44_58: UP
PE3#
*May 3 13:32:16.245: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 33_17: DOWN
*May 3 13:32:16.262: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 33_39: DOWN
PE4#
*May 3 13:29:16.792: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor 192.168.254.2:0 (1) is DOWN (Discovery Hello Hold Timer expired)
PE4#
*May 3 13:29:34.804: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 44_64: UP
*May 3 13:29:34.848: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 22_33: UP
PE4#
*May 3 13:29:39.592: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_13: UP
*May 3 13:29:39.603: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 11_46: UP
PE4#
*May 3 13:29:40.928: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 44_58: UP
*May 3 13:29:40.936: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_23: UP
*May 3 13:29:40.991: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.44 33_34: UP
PE4#
*May 3 13:29:43.885: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.255.255.2 on GigabitEthernet0/2.32 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
*May 3 13:29:43.896: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 444_11: DOWN
PE4#
*May 3 13:32:19.139: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.33 44_41: DOWN
*May 3 13:32:20.069: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.22 44_43: DOWN
PE4#
*May 3 13:32:23.717: %MPLS_TE-5-LSP: LSP 192.168.254.11 44_21: DOWN
Analizziamo gli output dei singoli tunnel dal punto di vista di PE1:
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22
Name: to-pe2 (Tunnel22) Destination: 192.168.254.22
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 20, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 3)
path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe2
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 20 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 24
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 22, Tun_Instance 23
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.2
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.29 1.1.1.30 1.1.1.45
1.1.1.46 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.1(24) 192.168.254.4(45)
192.168.254.22(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 3 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.29 1.1.1.30
1.1.1.45 1.1.1.46 192.168.254.22
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 35 minutes, 44 seconds
Time since path change: 30 minutes, 5 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 23
Current LSP:
Uptime: 30 minutes, 8 seconds
Selection: reoptimization
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 10 [21]
Removal Trigger: re-route path verification failed
Last Error: PCALC:: Can’t use link 1.1.1.6 on node 192.168.254.2
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 22 protection
to-pe2
LSP Head, Tunnel22, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.22, Instance 23
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 24, nhop: 1.1.1.1
nnhop: 192.168.254.4; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.4
Path Protection: None
PE1#
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 222
Name: to-pe2-backup (Tunnel222) Destination: 192.168.254.22
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 10, type explicit lsp-backup-22 (Basis for Setup, path weight 3)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: explicit path option 10 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 50
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.22, Tun_Id 222, Tun_Instance 11
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.25
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.17 1.1.1.18 1.1.1.45
1.1.1.46 192.168.254.22
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 3 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.29 1.1.1.30
1.1.1.45 1.1.1.46 192.168.254.22
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 39 minutes, 58 seconds
Time since path change: 38 minutes, 26 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 11
Current LSP:
Uptime: 38 minutes, 26 seconds
PE1#
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 33
Name: to-pe3 (Tunnel33) Destination: 192.168.254.33
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe3 (Basis for Setup, path weight 2)
path option 20, type dynamic
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: explicit path option 10 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.24, 16
FRR OutLabel : Tunnel333, explicit-null
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.33, Tun_Id 33, Tun_Instance 21
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.25
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.26 1.1.1.13 1.1.1.14 192.168.254.33
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.3(16) 192.168.254.33(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 2 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.37
192.168.254.33
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 41 minutes, 53 seconds
Time since path change: 40 minutes, 21 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 21
Current LSP:
Uptime: 40 minutes, 21 seconds
PE1#
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 33 protection
to-pe3
LSP Head, Tunnel33, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.33, Instance 21
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: FRR Ready
Backup Tu333 to LSP nnhop
Tu333: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 42
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.24, label: 16, nhop: 1.1.1.26
nnhop: 192.168.254.33, nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.33
With FRR: out i/f: Tu333, label: implicit-null
LSP bw: 0 kbps, Backup level: any-unlim, type: any pool
Path Protection: None
PE1#
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 333
Name: to-pe3-backup (Tunnel333) Destination: 192.168.254.33
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 10, type explicit lsp-backup-33 (Basis for Setup, path weight 2)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: explicit path option 10 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 42
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.33, Tun_Id 333, Tun_Instance 11
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.2
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.37 192.168.254.33
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 2 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.38 1.1.1.37
192.168.254.33
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 45 minutes, 1 seconds
Time since path change: 43 minutes, 30 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 11
Current LSP:
Uptime: 43 minutes, 30 seconds
PE1#
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 44
Name: to-pe4 (Tunnel44) Destination: 192.168.254.44
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 20, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 3)
path option 10, type explicit path-lsp-explicit-pe4
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: enabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 20 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : –
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/0.2, 48
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 192.168.254.11, Dst 192.168.254.44, Tun_Id 44, Tun_Instance 23
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 1.1.1.2
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.29 1.1.1.30 1.1.1.21
1.1.1.22 192.168.254.44
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: 192.168.254.1(48) 192.168.254.4(50)
192.168.254.44(0)
Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 3 (TE)
Explicit Route: 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.29 1.1.1.30
1.1.1.21 1.1.1.22 192.168.254.44
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 46 minutes, 31 seconds
Time since path change: 40 minutes, 46 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 23
Current LSP:
Uptime: 40 minutes, 49 seconds
Selection: reoptimization
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 10 [21]
Removal Trigger: re-route path verification failed
Last Error: PCALC:: Can’t use link 1.1.1.26 on node 192.168.254.3
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel 44 protection
to-pe4
LSP Head, Tunnel44, Admin: up, Oper: up
Src 192.168.254.11, Dest 192.168.254.44, Instance 23
Fast Reroute Protection: Requested
Outbound: Unprotected: no backup tunnel assigned
LSP signalling info:
Original: out i/f: Gi0/0.2, label: 48, nhop: 1.1.1.1
nnhop: 192.168.254.4; nnhop rtr id: 192.168.254.4
Path Protection: None
PE1#
Verifichiamo il risultato from PC1:
PC1> trace 20.20.20.20
trace to 20.20.20.20, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop
1 10.10.10.1 2.751 ms 2.014 ms 1.830 ms
2 1.1.1.1 26.984 ms 31.558 ms 29.561 ms
3 1.1.1.30 21.734 ms 21.275 ms 23.708 ms
4 20.20.20.1 23.410 ms 22.699 ms 20.109 ms
5 * * *
6 *20.20.20.20 35.187 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 30.30.30.30
trace to 30.30.30.30, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop
1 10.10.10.1 2.153 ms 1.823 ms 1.896 ms
2 1.1.1.26 16.957 ms 11.640 ms 13.962 ms
3 30.30.30.1 17.680 ms 13.039 ms 11.435 ms
4 * * *
5 *30.30.30.30 19.994 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
PC1> trace 40.40.40.40
trace to 40.40.40.40, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop
1 10.10.10.1 2.378 ms 2.258 ms 2.512 ms
2 1.1.1.1 27.011 ms 27.037 ms 19.096 ms
3 1.1.1.30 30.361 ms 24.779 ms 26.150 ms
4 40.40.40.1 22.900 ms 18.372 ms 19.499 ms
5 * * *
6 *40.40.40.40 22.523 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
Se sei interessato a vedere un SRTE Policy per la costruzione e la configurazione di Traffic Engineering con segment-routing vedi: https://www.massimilianosbaraglia.it/routing/segment-routing/segment-routing-teoria/srte-traffic-engineering-sr-policy-candidate-path